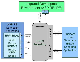
EPCIS Repository
Please note that the AspireRfid EPCIS Repository is a slightly modified version of Accada RFID Middleware, which is now call FossTrak, licensed under LGPL. AspireRfid have implemented changes and bug fixes on the original Accada middleware. As of 14/05/2009 we have ceased distribution of FossTrak licensed code. The AspireRfid EPCIS repository (under development) will be compatible with the Fosstrak EPCIS repository.
Introduction

- Receive application-agnostic RFID data from the filtering & collection middleware through the Business Event Generation (BEG) application.
- Translate RFID data in corresponding business events. These events carry the business context as well (e.g., they refer to particular companies, business locations, business processes etc.).
- Make business events available and accessible to other upstream applications.
- A capture application that interprets the captured RFID data.
- A repository (i.e. a database system) that provides persistence, and
- A query application that retrieves the business events from the repository.
- Deals explicitly with historical data (in addition to current data).
- Deals not just with raw RFID data observations, but also with the business context associated with these data (e.g., the physical world and specific business steps in operational or analytical business processes).
- Operates within enterprise IT environments at a level that is much more diverse and multi-faceted comparing to the underlying data capture and filtering & collection middleware modules.
- RFID event data i.e. data arising in the course of carrying out business processes. These data change very frequently, at the time scales where business processes are carried out.
- Master/company data, i.e. additional data that provide the necessary context for interpreting the event data. These are data associated with the company, its business locations, its read points, as well as with the business steps comprising the business processes that this company carries out.
Users Guide
Requirements
Hardware (minimum)- P IV 1.2GHz or equivalent
- 512 MB Ram
- 50 MB free HD space
- Java 1.6
- Tomcat 6.0 (or higher) or another server for web-services. (This guide assumes that you use an Apache Tomcat server.)
- MySQL 5.0 (or higher).
Deployment
This section includes a step-by-step tutorial describing how to set up your own EPCIS repository.In order to set up your own EPCIS repository, follow the step-by-step tutorial outlined below: Make sure you have an Apache Tomcat servlet container (version 6.0 or higher) running. It will be used to deploy and run the EPCIS repository web application. Download the latest aspireRfidEpcisRepository distribution found at the ASPIRE's Forge and place the WAR file contained in the archive in your Tomcat's webapps directory. After restarting Tomcat, the WAR file will be deployed. Install a MySQL server (version 5.0 or higher). It will be used by the EPCIS repository to store event data. Make sure that web applications deployed to Tomcat can access your MySQL server by installing the MySQL Connector/J driver. This is usually done by copying the mysql-connector-java-mysql> CREATE DATABASE epcis;
mysql> GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP, CREATE, ALTER ON epcis.* TO epcis IDENTIFIED BY 'epcis';
mysql> USE epcis; mysql> SOURCE <path-to-unpacked-download>/epcis_schema.sql
mysql> SOURCE <path-to-unpacked-download>/epcis_demo_data.sql
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <Context reloadable="true"> <Resource name="jdbc/EPCISDB" type="javax.sql.DataSource" auth="Container" username="epcis" password="epcis" driverClassName="org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver" url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/epcis?autoReconnect=true"> </Resource> </Context>
Runtime Configuration of your EPCIS Repository
In this section, we describe the properties you can use to configure AspireRFID EPCIS repository implementation.Basically there are three coniguration files relevant to the user of the application: application.properties, context.xml, and log4j.propertiesapplication.properties The application.properties file is located in the application's class path at TOMCAT_HOME/webapps/aspireRfidEpcisRepository/WEB-INF/classes. It contains the basic configuration directives that control the repository's behaviour when processing queries and events. This file looks as follows:# application.properties - various properties (loaded at runtime) which are used # to configure the behaviour of the epcis-repository application# the version of this service, as exposed by getVendorVersion (must be valid URI) service.version=http://wiki.aspire.objectweb.org/xwiki/bin/view/Main.Documentation/EpcisRepository# maximum number of result rows allowed for a single query before a # QueryTooLarge exception is raised maxQueryResultRows=1000# maximum time in milliseconds to wait for a query to finish before a # QueryTooComplex exception is raised maxQueryExecutionTime=20000# whether to allow inserting new vocabularies when they are missing in the db insertMissingVoc=true# the schedule used to check for trigger conditions - the values provided here # are parsed into a query schedule which is used to periodically check whether # incoming events contain a specific trigger URI trigger.condition.check.sec=0,20,40 trigger.condition.check.min=# whether to allow resetting the database via a HTTP POST 'dbReset' parameter dbResetAllowed=false dbResetScript=/sql/reset_epcis_with_demo_data.sql# the location of the EPCglobal EPCIS schema epcisSchemaFile=/wsdl/EPCglobal-epcis-1_0.xsd# the location of the EPCglobal EPCIS MasterData schema(nkef) epcisMasterDataSchemaFile=/wsdl/EPCglobal-epcis-masterdata-1_0.xsd# whether to trust a certificate whose certificate chain cannot be validated # when delivering results via Query Callback Interface trustAllCertificates=false# the name of the JNDI datasource holding the connection to the database jndi.datasource.name=java:comp/env/jdbc/EPCISDB
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <Context reloadable="true"> <Resource name="jdbc/EPCISDB" type="javax.sql.DataSource" auth="Container" username="epcis" password="epcis" driverClassName="org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver" defaultAutoCommit="false" url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/epcis?autoReconnect=true"> </Resource></Context>
# LOG4J configuration# default logging
log4j.rootCategory=INFO, LOGFILE# customize logging levels
log4j.logger.org.ow2.aspirerfid = DEBUG
log4j.logger.org.fosstrak = DEBUG
log4j.logger.org.accada = DEBUG
log4j.logger.org.ow2.aspirerfid = DEBUG# enable logging of SQL prepared statements
log4j.logger.org.hibernate.SQL=FINE
log4j.logger.org.hibernate.type=FINE# enable logging of incoming/outgoing SOAP requests/responses
log4j.logger.org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingInInterceptor=INFO
log4j.logger.org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingOutInterceptor=INFO# logging to file
log4j.appender.LOGFILE=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.LOGFILE.File=${catalina.base}/logs/aspireRfidEpcisRepository.log
log4j.appender.LOGFILE.DatePattern='.'yyyy-MM-dd'.log'
log4j.appender.LOGFILE.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.LOGFILE.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p (%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS}) [%C:%L] - %m%n
 PDF
PDF History
History